Introduction: What is a Computer?
- A computer is a programming machine designed to perform arithmetic and logical operations automatically and sequentially on the input given by the user and gives the desired output after processing
- The word computer has been originated from the Latin word ‘Computerae’ which means’ to compute’ or ‘to calculate’.

A computer can be defined as ” An automatic electronic device used for making a calculation or by manipulating controlling operations that are expressible in numerical or logical terms.”
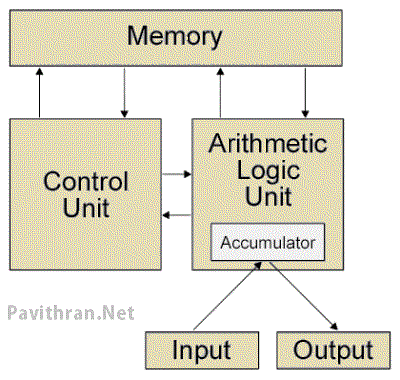
Major parts of the Computer
Input Devices
A device that can be used to insert data into a computer or other computational device is known as the Input device.
Keyboard:- it is an input device. it is used to do typing of alphabets and
numbers it looks like at an ordinary typewriter. It contains 101 or 104 keys.
The buttons on the keyboard can be classified:
- Alphabet keys
- Numeric keys
- Special character keys
- Special keys
- Function keys
Alphabet keys: – those keys which are used to do typing of letters ‘A’ to
‘Z’ called alphabetic keys
Numeric keys: – those keys which are used to do typing of digits ‘0’ to 9
are called numeric keys.
Special character keys: -those keys which are used to do typing of
special symbols +,-,x,/ etc are called special character keys
Special keys: – those keys which are used to send special signals to the
CPU is called special keys
Function keys: -there are 12 keys labeled as F1 to F12 are present at the
the first row of the keyboard. Those keys are used as a shortcut of instructions the function (work) at these keys depends upon the software being used. These keys are also called programmable keys.
Special keys and their work
Enter keys:- These keys used to move the cursor to the beginning of the next line or to get a result of instructions.
Space bar: – This key is used to put a blank space between two words.
Backspace:- This key is used to erase the character which is lost of
the current cursor position.
Caps lock:- This key is used to do typing of the capital letter it is also called
toggle key when it pressed for the first time it is turned on and when it is
pressed again it is turned off.
Cursor control keys:- These keys are used to move the cursor the pointing
direction.
Home keys: – These keys move the cursor to the beginning of the first line.
End key: – These keys move the cursor to the end of the line.
FULL-FORM OF COMPUTER
Computer is the Acronym of Commonly Operated Machine Particularly Used for Technology Education and Research
| C | Commonly |
| O | Operated |
| M | Machine |
| P | Particularly |
| U | Used for |
| T | Technology |
| E | Education & |
| R | Research |
- CPU = Central Processing Unit
- RAM = Random Access Memory
- ROM = Read Only Memory
- PROM = Programmable Read Only Memory
- EPROM = Erasable PROM
- EEPROM = Electrically EPROM
- HDD = Hard Disk Drive
- FDD = Floppy Disk Drive
- KBD = KeyBoard
- I/O = Input & Output
- CD = Compact Disk
- DVD = Digital Video Disk
- SMPS = Switch Mode Power Supply
- POST = Power ON Self Test
- BIOS = Basic Input Output System
- VDU = Visible Display Unit
- LED = Light Embedded Diode
- LCD = Liquid Crystal Display
- USB = Universal Serial Bus
- VGA = Video/Visual Graphic Adapter
- LAN = Local Area Network
- WAN = Wide Area Network
- MAN = Metropolitan Area Network
- HLL = High Level Language
- LLL = Low Level Language
- MIPS = Million of Instruction Per Second
- Mbps = Mega Bytes Per second
- Kbps = Kilo Bytes per second
- HTTP = Hyper Text Templates
- WWW = World Wide Web
- IP = Internet Protocol
- ISP = Internet Service Provider
- HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol.
- HTTPS – HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure.
- IP – Internet Protocol.
- URL – Uniform Resource Locator.
- USB – Universal Serial Bus.
- VIRUS – Vital Information Resource Under Seized.
- 3G – 3rd Generation.
- GSM – Global System for Mobile Communication.
- CDMA – Code Division Multiple Access.
- UMTS – Universal Mobile Telecommunication System.
- SIM – Subscriber Identity Module.
- AVI – Audio Video Interleave
- RTS – Real-Time Streaming
- SIS – Symbian OS Installer File
- AMR – Adaptive Multi-Rate Codec
- JAD – Java Application Descriptor
- JAR – Java Archive
- JAD – Java Application Descriptor
- 3GPP – 3rd Generation Partnership Project
- 3GP – 3rd Generation Project
- MP3 – MPEG player 3
- MP4 – MPEG-4 video file
- AAC – Advanced Audio Coding
- GIF – Graphics Interchangeable Format
- JPEG – Joint Photographic Expert Group
- BMP – Bitmap
- SWF – Shock Wave Flash
- WMV – Windows Media Video
- WMA – Windows Media Audio
- WAV – Waveform Audio
- PNG – Portable Network Graphics
- DOC – Document (Microsoft Corporation)
- PDF – Portable Document Format
- M3G – Mobile 3D Graphics
- M4A – MPEG-4 Audio File
- NTH – Nokia Theme (series 40)
- THM – Themes (Sony Ericsson)
- MMF – Synthetic Music Mobile Application File
- NRT – Nokia Ringtone
- XMF – Extensible Music File
- WBMP – Wireless Bitmap Image
- DVX – DivX Video
- HTML – HyperText Markup Language
- WML – Wireless Markup Language
- CD – Compact Disk.
- DVD – Digital Versatile Disk.
- CRT – Cathode Ray Tube.
- DAT – Digital Audio Tape.
- DOS – Disk Operating System.
- GUI – Graphical User Interface.
- IP – Internet Protocol.
- ISP – Internet Service Provider.
- TCP – Transmission Control Protocol.
- UPS – Uninterruptible Power Supply.
- HP – Hewlett Packard.
- AM/FM – Amplitude/ Frequency Modulation.
- WLAN – Wireless Local Area Network
- AVI – Audio Video Interleave
- RTS – Real-Time Streaming
- SIS – Symbian OS Installer File
- AMR – Adaptive Multi-Rate Codec
- JAD – Java Application Descriptor
- JAR – Java Archive
- JAD – Java Application Descriptor
- 3GPP – 3rd Generation Partnership Project
- 3GP – 3rd Generation Project
- IP – Internet Protocol.
- ISP – Internet Service Provider.
- TCP – Transmission Control Protocol.
- UPS – Uninterruptible Power Supply.
- URL – Uniform Resource Locator.
- USB – Universal Serial Bus.
- VIRUS – Vital Information Resource Under Seized.
- 3G – 3rd Generation.
- GSM – Global System for Mobile Communication.
- CDMA – Code Division Multiple Access.
- UMTS – Universal Mobile Telecommunication System.
- SIM – Subscriber Identity Module.
- HSDPA – High-Speed Downlink Packet Access.
- EDGE – Enhanced Data Rate for
- GSM – [Global System for Mobile Communication] Evolution.
- VHF – Very High Frequency.
- UHF – Ultra High Frequency.
- GPRS – General Packet Radio Service.
- WAP – Wireless Application Protocol.
- TCP – Transmission Control Protocol.
- ARPANET – Advanced Research Project Agency Network.
- IBM – International Business Machine Corporation.
- 4 Bits = 1 Nibble
- 8 Bits = 1 Byte
- 1024 Bytes = 1 Kilo Byte ( KB )
- 1024 KB = 1 Mega Byte ( MB )
- 1024 MB = 1 Gyga Byte ( GB )
- 1024 GB = 1 Tera Byte ( TB )
- 1024 TB = 1 Peta Byte ( PB )
- 1024 PB = 1 Exa Byte ( EB )
- 1024 EB = 1 Zetta Byte ( ZB )
- 1024 ZB = 1 Yotta Byte ( YB )
Categorization on the basis of generation
First Generation(1940-1956): computers used Vacuum tubes.
Second Generation(1956-1963): computers used Transistor
Third Generation(1964-1971): computers used Integrated Circuits
Fourth Generation(1971- Present): computers used Microprocessors
Fifth-generation(Present and Beyond): computers based on Artificial Intelligence
There are many types of computers available on the basis of their working areas: Supercomputer, work frames, personal computers, desktops, laptops, palmtops, etc.
Useful Books for Competitive Exams
Best Books for Competitive Exams [PDF]
Disclaimer: Pavithran.Net doesn’t aim to promote or condone piracy in any way. We do not own any of these books. We neither create nor scan this Book. The Images, Books & other Contents are copyrighted to their respective owners. We are providing PDFs of Books that are already available on the Internet, Websites, and Social Media like Facebook, Telegram, Whatsapp, etc. We highly encourage visitors to Buy the Original content from their Official Sites. If any way it violates the law or if anybody has Copyright issues/ having discrepancies over this post, Please Take our Contact Us page to get in touch with us. We will reply as soon as we receive your Mails.
We Need Your Support. Please Share the Link if it is helpful to your Cherished circle


![YCT Computer Planner Chapterwise Solved Papers [English Medium] 2024-25](https://www.pavithran.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/YCT-Computer-Planner-Chapterwise-Solved-Papers-English-Medium-2024-25-741x1024.webp)

![Computer Hindi eBook [X-EEED Publication]](https://www.pavithran.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Computer-Hindi-eBook-X-EEED-Publication-824x1024.webp)



![StudyIQ General Awareness Book [2022 Edition] - English Medium](https://www.pavithran.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/StudyIQ-General-Awareness-Book-2022-Edition-English-Medium-150x150.webp)

![Arihant GK 2025 - Manohar Pandey [Small Edition]](https://www.pavithran.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Arihant-GK-2025-Manohar-Pandey-Small-Edition-150x150.webp)